December 10, 2021
In
News, Press release
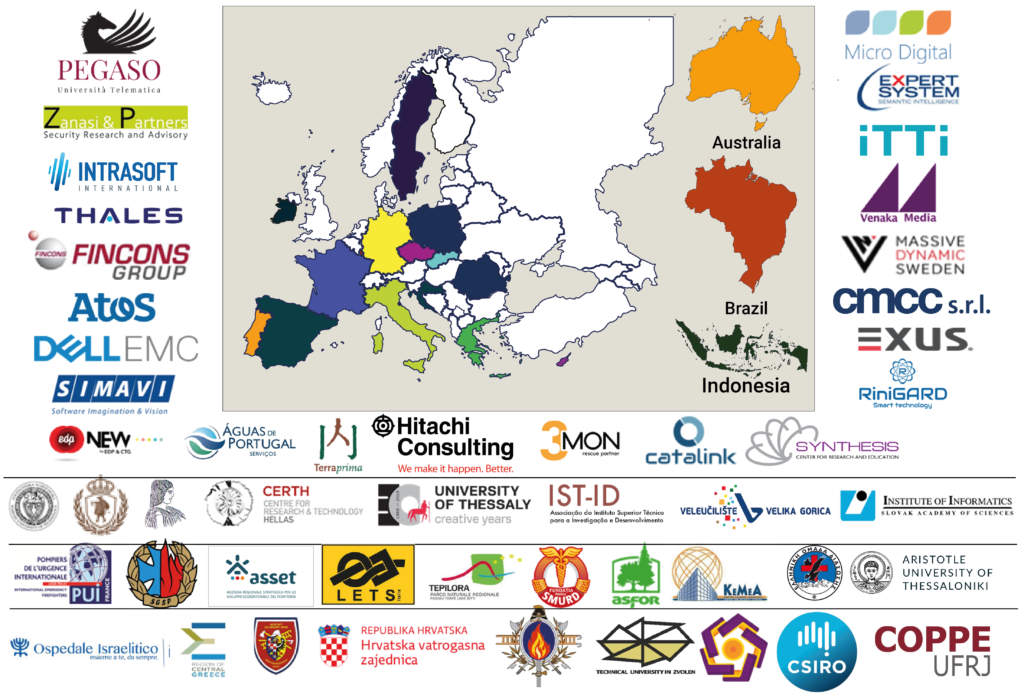
Funded by the EU Horizon 2020 Green Deal program and coordinated by Università Telematica Pegaso, SILVANUS project includes 49 partners from the European Union, Brazil, Indonesia, and Australia, with a budget of €23 million for a period of 42 months.
The SILVANUS project brings together a large consortium of interdisciplinary experts from four continents to combat the threat of forest fires and improve forest resilience against climate change.
The key output of the project is the release of a climate resilient forest management platform to prevent and suppress forest fire. SILVANUS relies on environmental, technical and social sciences experts to support regional and national authorities responsible for wildfire management in their respective countries. SILVANUS scientists and research engineers will aid the civil protection authorities to efficiently monitor forest resources, to evaluate biodiversity, to generate more accurate fire risk indicators, and promote safety regulations among the local population affected by wildfire through awareness campaigns.
What makes SILVANUS innovative?
In the climate crisis era, where forest fires are becoming more dangerous and more frequent, SILVANUS aims to offer a new technological solution to improve the preparedness and prevention of wildfire ignition. This will be achieved through the integration of big-data processing framework capable of analysing various data sources such as climate models, weather data, and earth observation tools, leading to the development of intelligent fire ignition models. These models will be furthermore complemented with the use of in-situ environmental sensors, CCTV and multi-spectral imaging solutions to develop an advanced detection and response toolkit. SILVANUS will also introduce sensor technologies that use inventive wireless communication infrastructure through the coordination of unmanned aerial vehicles and automated ground robots for coordinating the response among first fighters.
The important aspect of the project is to consider the expertise and experience of firefighters and the local residents who are faced every year with the dangers of devastating wildfires. SILVANUS will launch a wide-reaching stakeholder engagement programme in forest regions to assess fire risk indicators, to develop training methodology for firefighters, to use for VR and AR training toolkits, and to simulate real-world environments and life-saving scenarios. Awareness campaigns will include the implementation of mobile application for citizen engagement, along with automated notifications on safety practices.
Pilot implementation and long-term impacts
The SILVANUS project innovations will be systematically deployed and demonstrated across eight EU Member States regions (France, Italy, Slovakia, Greece, Czechia, Portugal, Croatia, and Romania). Additional demonstrations will also be carried out across Indonesia, Brazil, and Australia.
To ensure that the results of SILVANUS have a long-term impact, the project will include policy recommendations on forest governance, soil rehabilitation strategy recommendation, and restoration roadmap services for natural resources.
For the duration of its activities and beyond, SILVANUS will focus on all three components of fire suppression: prevention and preparedness, detection and response, restoration and adaptation.
The SILVANUS project will kick off with a hybrid meeting in Naples, Italy, scheduled on the 13th and 14th of December 2021. Please stay tuned for further updates on the project progress.
Additional info at: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/101037247
Partners
Università Telematica Pegaso (Pegaso Telematic University), Zanasi&Partners, INTRASOFT International SA, Thales, Fincons Spa, Atos IT Solutions and Services Iberia SL, Dell Technologies, Software Imagination & Vision SRL, CNET Centre for New Energy Technologies SA, AdP Valor – Serviços Ambientais, S.A., Terraprima – Serviços Ambientais Sociedade Unipessoal LDA, 3MON, s.r.o., Catalink Limited, Synthesis Center for Research and Education Limited, Expert.AI SpA, ITTI Sp. z o.o., Venaka Treleaf GbR, Massive Dynamic Sweden AB, Fondazione Centro Euro-Mediterraneo sui Cambiamenti Climatici (Euro-Mediterranean Center on Climate Change), EXUS Software Monoprosopi Etairia Periorismenis Evthinis, RiniGARD d.o.o., Micro Digital d.o.o., Politechnika Warszawska (Warsaw University of Technology), Högskolan I Borås (University of Borås), Geoponiko Panepistimio Athinon (Agricultural University of Athens), Centre for Research and Technology Hellas (CERTH) – Information Technologies Institute, Panepistimio Thessalias (University of Thessaly), Associação do Instituto Superior Técnico Para a Investigação e Desenvolvimento (IST-ID), Veleučilište Velika Gorica (University of Applied Sciences Velika Gorica), Ústav Informatiky Slovenska Akademia VIED (Insitute of Informatics – Slovak Academy of Sciences), Pompiers de l’urgence Internationale (PUI France), The Main School of Fire Service Poland, Agenzia regionale Strategica per lo Sviluppo Ecosostenibile del Territorio (Regional Strategic Agency for the Eco-sustainable Development of the Territory), LETS Italia SRLS, Parco Naturale Regionale di Tepilora (Regional Natural Park of Tepilora), Fundația Pentru SMURD (SMURD Foundation), Asociația Forestierilor din România (Romainan Forestry Association – ASFOR), Kentro Meleton Asfaleias (Center for Security Studies – KEMEA), Elliniki Omada Diasosis Somateio (Hellenic Rescue Team – HRT), Aristotelio Panepistimio Thessalonikis (Aristotle University of Thessaloniki), Ospedale Israelitico (Jewish Hospital Rome), Region of Sterea Ellada (Central Greece), Hasicsky zachranny sbor Moravskoslezskeho kraje (Fire Rescue Brigade of Moravian-Silesian Region), Hrvatska vatrogasna zajednica (Croatian Firefighting Community), Technická Univerzita vo Zvolene (Technical University in Zvolen), Občianske Združenie Plameň Badín (Plamen), Yayasan AMIKOM Yogyakarta (University of AMIKOM Yogyakarta), Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (Federal University of Rio de Janeiro)